Introduction
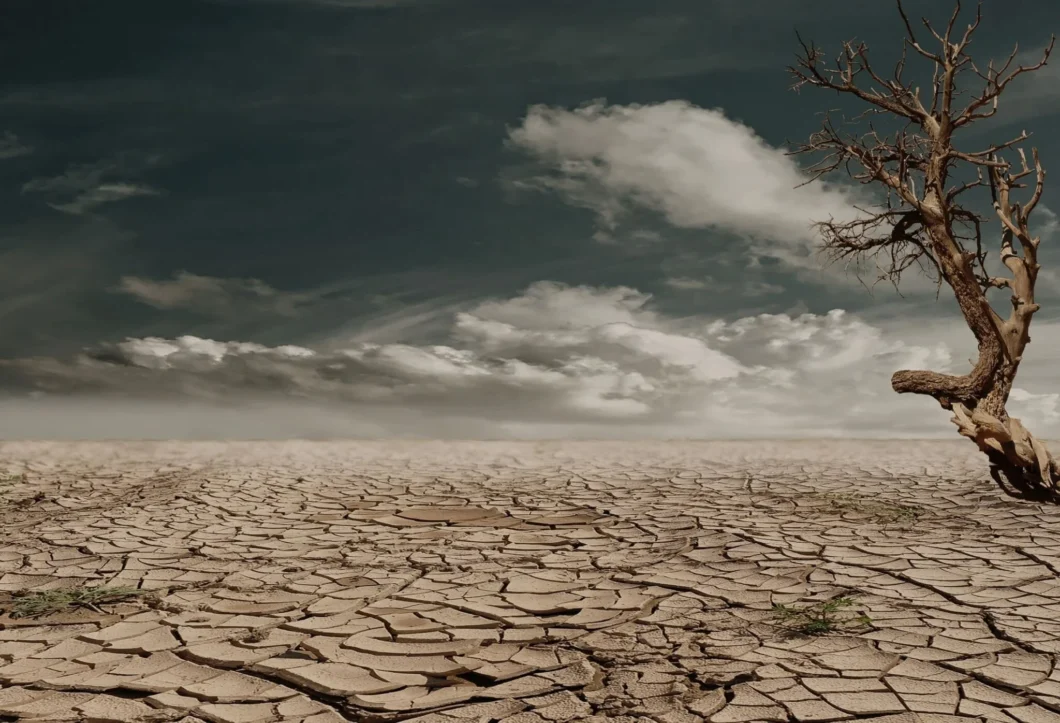
Have you ever heard the old saying, “Old habits die hard.”? While it might seem like a harmless cliché, there’s an undeniable truth underlying those words. Bad habits, those subtle behaviors that often go unnoticed in our daily lives, have the potential to create chaos on our progress and personal development. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what bad habits are, why they are so detrimental, and how they lead to regression rather than growth.
Understanding Bad Habits
A habit is a routine behavior that is repeated regularly and often unconsciously. Some habits can be positive, contributing to our well-being and success, while others, known as bad habits, can have a negative impact on our lives. Bad habits are those behaviors that do not allow us to progress, deteriorate our health, or become an obstacle to our personal growth.
Bad habits can take many forms, ranging from seemingly minor actions like procrastination, excessive smartphone use, and nail-biting, to more serious habits like smoking, overeating, and negative self-talk. What sets bad habits apart is their negative impact on our lives over time.
The Regression Trap
So, why do bad habits lead to regression? The answer lies in the way our brains are wired and the patterns these habits create.
Instant Gratification vs. Long-Term Goals: Bad habits often provide instant gratification, giving us a quick hit of pleasure or relief. This immediate reward can trick our brains into seeking these behaviors repeatedly, even if they conflict with our long-term goals. For example, binge-watching a TV show might feel good in the moment, but it can hinder productivity and progress toward professional or personal goals.
Neuroplasticity and Reinforcement: Our brains are remarkably adaptable. When we repeat a behavior, our brain’s neural pathways strengthen, making it easier to engage in that behavior again. Bad habits exploit this neuroplasticity, creating a cycle where the more we engage in the habit, the harder it becomes to break it. This process makes regressing into the habit more likely than progressing toward positive change.
Cognitive Dissonance: Bad habits often create cognitive dissonance – a mental discomfort caused by holding conflicting beliefs or attitudes. For instance, someone who knows the importance of regular exercise but consistently avoids the gym might experience cognitive dissonance. To ease this discomfort, individuals may justify their bad habits, reinforcing the negative behavior instead of confronting it.
Negative Impact on Self-Esteem: Consistently engaging in bad habits can erode our self-esteem and self-confidence. We may feel powerless to overcome these behaviors, leading to a cycle of defeatism and regression. This decline in self-esteem can further perpetuate the habit, as individuals turn to it for momentary relief from negative emotions.
Breaking the Cycle
Recognizing the destructive nature of bad habits is the first step toward breaking the cycle of regression. Here are a few strategies to help you overcome bad habits and foster positive change:
Self-Awareness: Reflect on your behaviors and identify the habits that are hindering your progress. Awareness is key to initiating change.
Set Clear Goals: Define your long-term goals and break them down into smaller, achievable steps. Focus on the positive outcomes you want to achieve.
Replace with Positive Habits: Replace bad habits with positive ones that align with your goals. Instead of mindlessly scrolling through social media, dedicate that time to reading, learning, or exercising.
Accountability: Share your goals and progress with a friend or family member who can provide support and hold you accountable.
Mindfulness: Practice mindfulness techniques to become more attuned to your behaviors and emotions. This can help you recognize triggers for bad habits and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
Conclusion
The road to personal growth and progress is paved with challenges, and bad habits can be major roadblocks along the way. The key to avoiding regression lies in understanding the psychology behind bad habits and actively working to replace them with positive behaviors. By breaking free from the cycle of instant gratification and embracing self-awareness, discipline, and determination, you can ensure that your journey remains one of growth, rather than regression. Remember, change is possible, and it starts with a commitment to breaking free from the chains of bad habits.